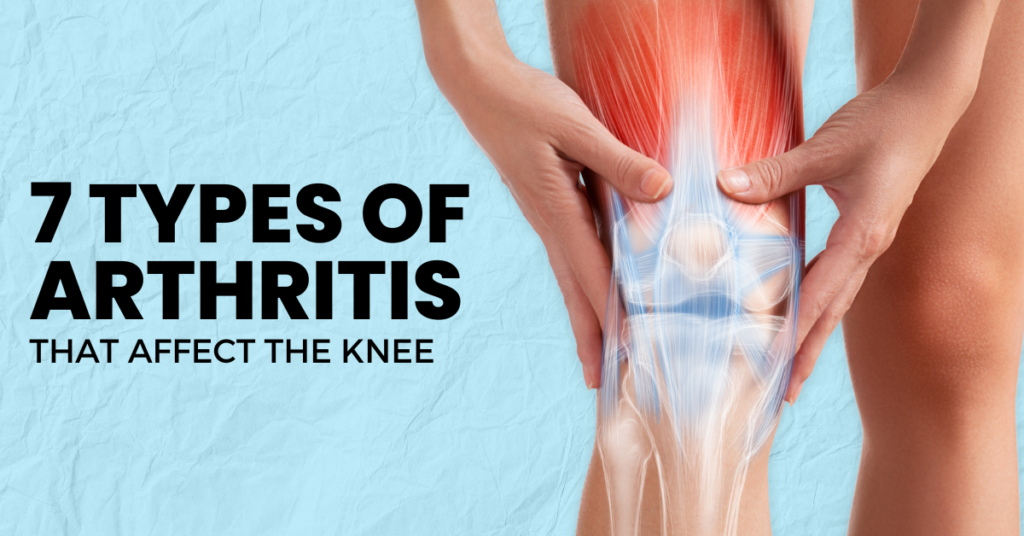
Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation and pain in the joints, and the knee, being one of the largest and most used joints in the body, is particularly susceptible to this ailment. Each type of arthritis has its own unique characteristics and treatment methods. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the seven main types of arthritis that can impact the knee, providing insights into their symptoms, causes, and treatments.
1. Osteoarthritis (OA)
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis and is primarily characterized by the wear and tear of the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones. As the cartilage deteriorates, the bones begin to rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, and reduced mobility.
Symptoms:
- Pain that worsens with activity
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after resting
- Swelling around the knee
- A grinding sensation when moving the knee
Treatment:
- Weight management to reduce stress on the knee
- Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee
- Pain relief medications, such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs
- In severe cases, surgery may be necessary, such as knee replacement
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, leading to inflammation. Unlike OA, RA can affect multiple joints and may lead to severe joint damage if left untreated.
Symptoms:
- Warm, swollen, and tender joints
- Symmetrical joint involvement (both knees may be affected)
- Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
- Fatigue and fever
Treatment:
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow progression
- Biologics that target specific parts of the immune system
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Physical therapy and exercise
3. Post-Traumatic Arthritis
What is Post-Traumatic Arthritis?
Post-traumatic arthritis develops after an injury to the knee, such as a fracture, ligament tear, or meniscus injury. These injuries can damage the cartilage and alter the knee’s movement, leading to arthritis.
Symptoms:
- Persistent pain following a knee injury
- Swelling and tenderness
- Instability or weakness in the knee
- Decreased range of motion
Treatment:
- Physical therapy to regain strength and mobility
- Pain relief medications
- Injections, such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid
- Surgery if the arthritis is severe
4. Gout
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joint. Although it usually affects the big toe, it can also occur in the knee. Gout attacks can be sudden and extremely painful.
Symptoms:
- Intense, sharp pain in the knee
- Swelling and redness
- The knee may feel hot to the touch
- Sudden onset, often at night
Treatment:
- Medications to reduce uric acid levels
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to manage pain during attacks
- Lifestyle changes, such as diet modifications to avoid foods high in purines
- Staying hydrated to help flush uric acid from the body
5. Pseudogout
What is Pseudogout?
Pseudogout, also known as calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease, is similar to gout but is caused by calcium crystals in the joint instead of uric acid crystals. It often affects the knee and can be very painful.
Symptoms:
- Sudden, severe pain in the knee
- Swelling and warmth around the knee
- Stiffness and decreased mobility
- The knee may feel tender to the touch
Treatment:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation
- Colchicine to prevent future attacks
- Regular exercise and physical therapy
6. Psoriatic Arthritis
What is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is a form of arthritis that affects some people with psoriasis, a condition that causes red, scaly skin patches. It can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling in any part of the body, including the knee.
Symptoms:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Stiffness, especially in the morning
- Red, scaly skin patches (psoriasis)
- Changes in the nails, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed
Treatment:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow progression
- Biologics to target specific immune responses
- Physical therapy and exercise to maintain joint function
7. Septic Arthritis
What is Septic Arthritis?
Septic arthritis is an infection in the joint, and it is a serious condition that can cause severe damage to the cartilage and bone if not treated promptly. It often affects large joints like the knee.
Symptoms:
- Severe pain in the knee
- Swelling and redness
- Fever and chills
- Difficulty moving the knee
Treatment:
- Immediate medical attention to prevent permanent damage
- Antibiotics to fight the infection
- Drainage of the infected joint
- Rest and possibly physical therapy after the infection is controlled
Conclusion
Arthritis of the knee can come in many forms, each with its own unique set of symptoms and treatments. Understanding the type of arthritis affecting your knee is crucial for effective management. If you experience persistent knee pain, swelling, or stiffness, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. By taking proactive steps, you can manage your symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
If you need personalized advice or treatment options, consider consulting with specialists who can provide targeted care for your condition. Keeping yourself informed and seeking timely medical attention can significantly impact your overall well-being and mobility.